GMAO and NCCS Provide Forecasts for 10 NASA Field Campaigns
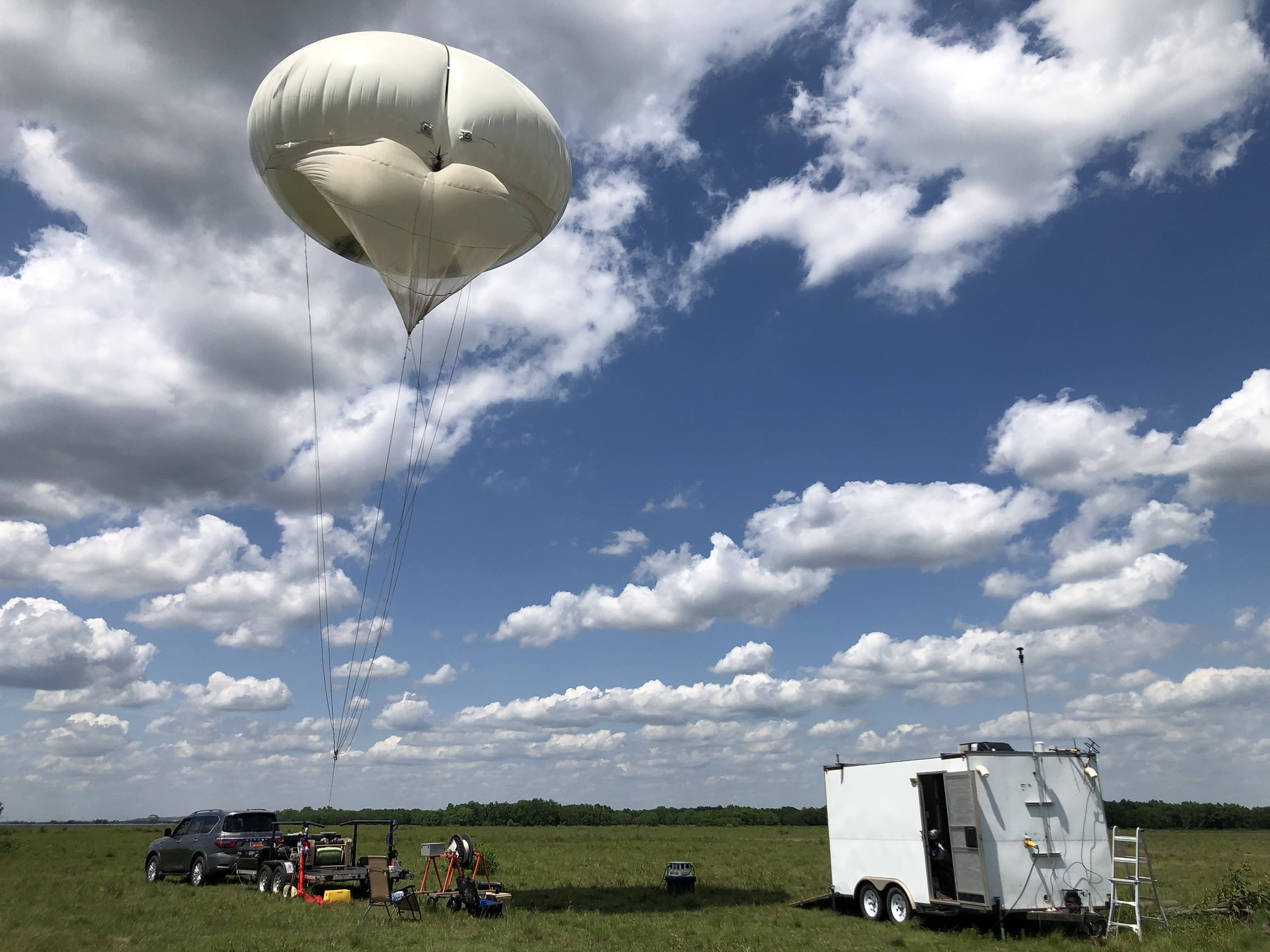

A tethered balloon system is flown at Guy, Texas, as part of the TRacking Aerosol Convection interactions ExpeRiment (TRACER). The TRACER field campaign aims to collect data on the evolution of convective clouds and the environment at locations around Houston, Texas. Photo by Brent Peterson, Sandia National Laboratories. Image courtesy of the U.S. Department of Energy Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility.
This year, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center’s Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) and NASA Center for Climate Simulation (NCCS) are providing near real-time atmospheric weather and chemistry forecasts for 10 NASA field campaigns — the largest number of supported campaigns since 2017.
These field campaigns are taking place across the U.S. and Canada, the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea, and South Korea as well as in low-Earth orbit. They include five new campaigns.
| Campaign Name | Campaign Dates | GMAO Support Page |
|---|---|---|
| ACTIVATE Aerosol Cloud meTeorology Interactions oVer the western ATlantic Experiment |
Nov 30, 2021–Jun 18, 2022 | |
| BlueFlux* Blue Carbon Prototype Products for Mangrove Methane and Carbon Dioxide Fluxes |
Mar 19, 2022–Oct 15, 2022 | BlueFlux Portal |
| DCOTSS Dynamics and Chemistry Of The Summer Stratosphere |
Apr 26, 2022–Jun 30, 2022 | DCOTSS Portal |
| TRACER* TRacking Aerosol Convection ExpeRiment |
May 29, 2022–Oct 01, 2022 | TRACER Portal |
| ABoVE Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment |
Jul 04, 2022–Aug 23, 2022 | ABoVE Portal |
| HIWC* High Ice Water Concentration |
Jul 05, 2022–Aug 01, 2022 | HIWC Portal |
| CAROb Cloud-Aerosol-Rain Observatory |
Jul 07, 2022– Sep 30, 2022 | CAROb Portal |
| ACCLIP Asian Summer Monsoon Chemical and Climate Impact Project |
Jul 18, 2022– Sep 11, 2022 | ACCLIP Portal |
| CPEX-CV Convective Processes Experiment — Aerosols & Winds |
Aug 22, 2022–Oct 15, 2022 | CPEX-CV Portal |
| LOFTID* Low-earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator |
Nov 1, 2022–TBD |
The Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) and NASA Center for Climate Simulation (NCCS) are supporting these 10 NASA field campaigns during 2022. A star (*) marks a new campaign.
The campaigns are leveraging two GMAO global forecasting systems running on the NCCS Discover supercomputer:
- Goddard Earth Observing System Forward-Processing (GEOS-FP), 12- and 25-kilometer (km) resolution, four times per day, 8,400 processor cores.
- GEOS-Composition Forecast (GEOS-CF), 25-km resolution, once per day, 3,510 processor cores.
Customized forecast data and visualizations are available for campaign planning and data analysis on the NCCS-hosted GMAO FLUID website (eight campaigns) and the NCCS DataPortal (two campaigns).
“The NCCS Discover and DataPortal teams work closely with GMAO operations staff to ensure the resources are available to support these missions,” said GMAO scientific programmer Robert Lucchesi. “The compute-intensive GEOS-FP and GEOS-CF systems require priority access to thousands of high-performance cores on Discover to generate these products, and the NCCS DataPortal provides the results to mission science teams."
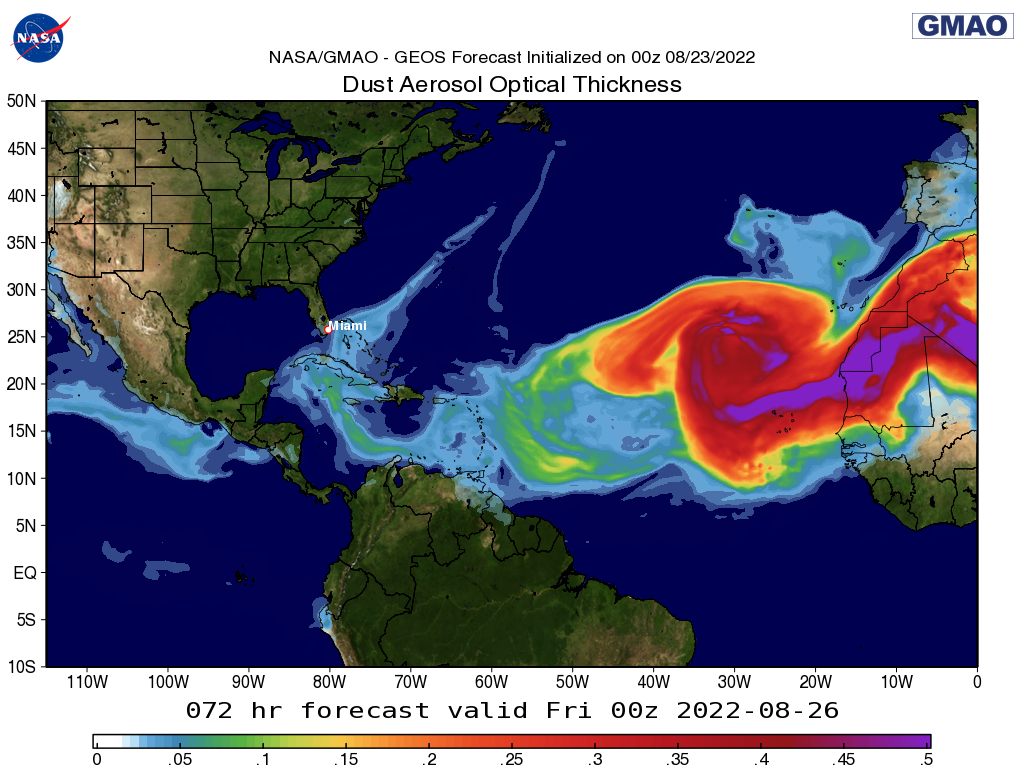
NASA GEOS-FP-predicted dust aerosol optical depth for August 26, 2022 (initialized August 23, 2022) over the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean, one example of forecasts provided for the Cloud-Aerosol-Rain Observatory (CAROb) field campaign. CAROb, located 4 kilometers offshore of Miami, Florida, is an instrumentation suite dedicated to characterizing the local cloud and aerosol environment, towards improving understanding of shallow cloud behavior and its interactions with the local thermodynamic, dynamic, and aerosol environment. Figure by GMAO.
Related Links
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO): NASA Field Campaigns Supported by GMAO.
- “NASA Field Campaigns Resume with GMAO and NCCS Support,” NCCS Highlight, September 29, 2021.
Jarrett Cohen, Christine Bloecker, and Robert Lucchesi, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
September 29, 2022.


